
When you build a website, there are two major aspects to consider: consumers and search engines.
You need an SEO-friendly website so you show up on Google when consumers are searching for your products. But you also need a creative, user-friendly website so consumers can find what they want to buy.
The conflict for site owners, especially when there are hundreds of products available on the site, becomes finding a balance between being user-friendly and SEO friendly. To further complicate things, many businesses have two separate teams for SEO and web development. Even if both teams are in-house, having them work together to build a beautiful and successful website can be challenging. The development team will fight to keep the visual and user aspect of the site very simplistic, while the SEO team will want to ensure the site has enough content so Google can rank it effectively for user search queries.
So how do you find the balance when you have conflicting suggestions coming from each side?
In this article, we’ll take a deeper look at what SEO web design is, why it’s important, and what 10 things you need to optimize to find some common ground between these two goals.
What is SEO web design?
SEO (or search engine optimization) is the practice of optimizing a website so that it ranks well on search engines. Website design is the design and creation of a website and all of its pages.
If you put them together, SEO web design is the design and creation of a website that is optimized for search engines. It covers the SEO best practices that designers need to follow when building websites.
Why is SEO web design important?
If your company website has a stunning design but you can’t get any of its web pages to rank in search engine results, how are people going to find your website?
While social media and PPC ads are great for increasing traffic, it’s important to find organic (read: free) ways to ramp up your website traffic and get to page one of the SERPs (search engine result pages).
Let’s go over a few of the top benefits of SEO web design.
SEO web design increases organic traffic
Organic traffic to your website is any kind of traffic coming from search engines that hasn’t been paid for. These are website viewers who found your site after searching for something on Google and browsing through the top options.
To be specific, the first search result gets over a quarter of all clicks, the second search result gets 15 percent, and it drops off quickly from there.

Since the 10th result gets 2.5 percent of the clicks, it’s safe to assume that anything past page one has abysmal organic traffic results. This is why you want to design and optimize your website as well as possible to increase the chances that you rank higher on SERPs.
SEO web design attracts high-intent traffic
When someone is conducting a Google search, it’s because they have a specific query they’re hoping to find information about. And when your page shows up at the top of the search results with that exact answer, they’re going to click over to your page.
While they may not convert right after discovering your website, they’re now aware that they can come back to you if they have any other related questions. This top-of-mind brand awareness is ideal for increasing conversions, all because they were searching for something in your industry.
Having that high-intent traffic is even more valuable than other traffic, which is why it’s important to optimize your new website to increase search engine rankings.
SEO web design improves the user experience
Every dollar invested in UX brings 100 in return, an ROI of 9,900 percent—but that’s not the only benefit. If you want to get on the good side of Google’s algorithm, your website needs to be SEO-optimized but also user-friendly. Google has refined its criteria so that user experience-related metrics factor into your rankings.
Based on studies done by Backlinko, some of these criteria include:
- Dwell time
- Mobile usability
- Bounce rate
Improving your website SEO is an essential part of any marketing strategy. It ensures your website works well and is easy for a visitor to navigate, so they can find the information they’re looking for.
Google only wants to rank the best sites to prevent its own user experience from being impacted by poor websites. So having a high-ranking site builds trust with the user while helping them find exactly what they’re looking for.
SEO web design gets the most from your marketing budget
An SEO strategy can take some time to implement, but the changes tend to be free. Many business owners can put SEO parameters in place themselves with a little bit of website knowledge, or they can defer it to someone on their team.
The point is that SEO is a low-cost strategy for helping your website to reach your marketing goals and increase your overall ROI.
10 things to optimize for SEO web design
Now that you know why SEO web design is so important, let’s talk about how you can optimize your website. Keep search engine optimization top of mind throughout the entire web design process to make implementing these 10 items as seamless as possible.
After all, you don’t want your web development team to create the entire website only to have your SEO team tear it apart and make the process take even longer. Instead, having the two teams work together on each of these items during the design process helps streamline the entire project.
Google’s search algorithm uses more than 200 factors to rank a website. It’s hard for any one designer to account for all. Instead, start by optimizing the following 10 elements to get your pages ranking:
- Mobile-friendliness
- Website speed
- Sitemaps
- Readability
- Image file names
- Alt tags
- Website navigation
- URL structure
- Metadata
- Indexable content
1. Mobile-friendliness
In 2021, 55 percent of all worldwide traffic came from mobile. By 2025, it’s expected that three quarters of the world will use only smartphones to access the web.
Having a responsive website helps improve your SEO, but also ensures your target audience has a seamless experience regardless of if they’re accessing your site from their computer or mobile device.
Let’s take a look at this website example from The Sill. They’re ranking on page one for keywords like plants, house plants, and where to buy house plants.
Its desktop website looks like this:
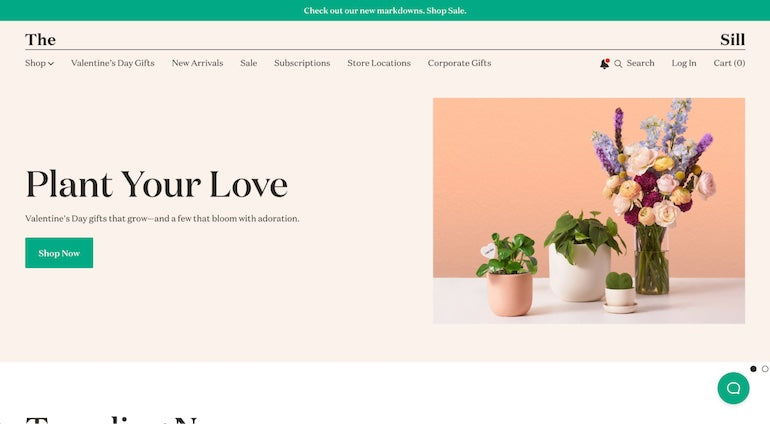
And its mobile website looks like this:

The mobile version is still easy to navigate and keeps the same flow of searching for products and heading to checkout, which is intuitive for an ecommerce site.
As you design your website, make sure you or your development team test that it works on both desktop and mobile. This is an essential ranking factor because Google released a mobile-friendly update to their algorithm back in 2015 that boosts responsive sites in search results.
2. Website speed
As of 2018, your website speed is yet another item that factors into Google’s algorithm. It makes sense—no one wants to deal with a website that takes ages to load. So Google won’t show it to them.
Things that can affect your page speed include:
- Web hosting
- File sizes
- Plugins
- Coding/scripts
- Traffic volume
Luckily, Google offers a free PageSpeed Insights tool that lets you insert your website URL and see where you stand.

Your website will get a different score for both desktop and mobile, along with several metrics to help you pinpoint how you can improve your page speed, and therefore, your rankability.
3. Sitemaps
While Google is very smart, it’s never a bad idea to give them a helping hand. And that’s exactly what a sitemap is for.
A sitemap is a file that houses all of your web pages, files, videos, and everything else that lives on your website. These are handy for websites with a lot of different pages, especially if they’re not all linked to other pages on your website.
This helps Google to find and crawl all of your web pages so they’re all eligible for ranking. After all, if Google can’t find a web page, it’s not going to generate any organic traffic.
4. Readability
Another major ranking factor is readability. If your website visitors can’t read the copy on your site, they’re not getting anything valuable from your business.
Best practices say that big, bold serif, or sans serif fonts should be used throughout your website, its headers, and its copy blocks to ensure it’s easy to read.
Look at this bold, clean website home page and how easy it is to read its headline and website copy:

Users immediately are able to grasp what Teachable can help them with. In addition, having your copy structured with heading tags supports Google in identifying the most important parts of each page, further improving your SEO.
If you use script fonts (i.e., if they’re a part of your branding), it’s best to do so only as an accent font, as we see in this example from Edloe Finch:
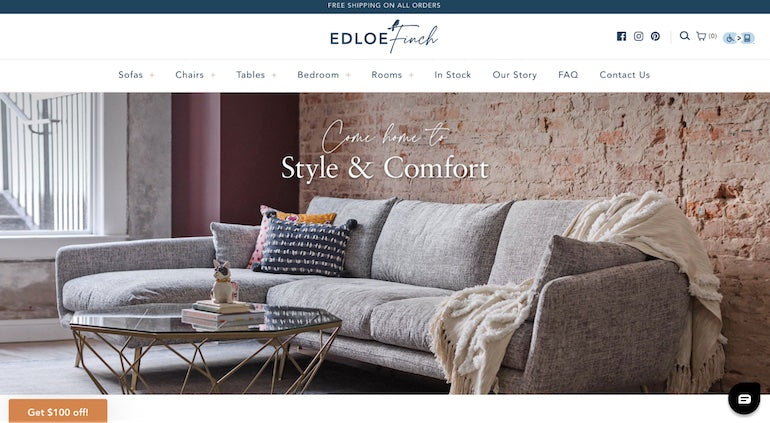
5. Image file names
Image file names are so small you might not even think about it, but they can actually be a big asset to your website optimization. So think twice before you name something home-page-header-final-2.jpg.
Instead, include keywords and descriptors that give Google an idea of what is featured in the image.
For example, in this section on Method’s website, image file names could be:
- aluminum-hand-wash-bottle.jpg,
- refillable-soap-pouches.jpg,
- rainbow-cleaning-products.jpg.

6. Alt tags
In a similar vein, your images also need to have alt tags. This is important for a number of reasons.
One, images are returned for nearly 25 percent of Google search queries. Data shows that the majority of younger searchers (62 percent) want visual search capabilities over any other technology.
Alt tags let Google’s algorithm know exactly what is going on in your images. If it matches a user’s search, your image could show up in their results.
Your alt tag should be a complete sentence that describes exactly what is in your image, complete with a capital letter at the beginning of your sentence and a period at the end.
Second, it improves your overall accessibility. Someone using a screen reader to access your website is able to understand what is depicted in your images, helping those who are visually impaired to still have a stellar user experience.
7. Website navigation
Web developers are typically focused on the site’s overall look, feel, and user experience. Designers and developers will care about a page’s visual elements and how consumers interact with those elements. They often like to keep things as simple as possible, especially since consumers using mobile devices have long surpassed consumers using desktop or laptop devices.
But crucially, your website navigation also provides internal links to your most important product or feature pages.
Take a look at this example from Visme.

Their navigation has dropdown menus leading to the most important pages on their website. This helps increase the number of internal links for each of the pages included in the navigation. This is because each page with this navigation counts as a unique internal link, increasing the number of overall links exponentially.
To rank higher on SERPs, these subcategory pages should target the keywords they’re hoping to rank for.
When you consider large ecommerce sites with hundreds or thousands of products, site navigation becomes even more critical.
REI’s website is a great example of SEO-friendly site navigation—they have a very large navigation for each category on the site. For example, when you click on the ‘Snow’ category, you get a massive list of subcategory pages.
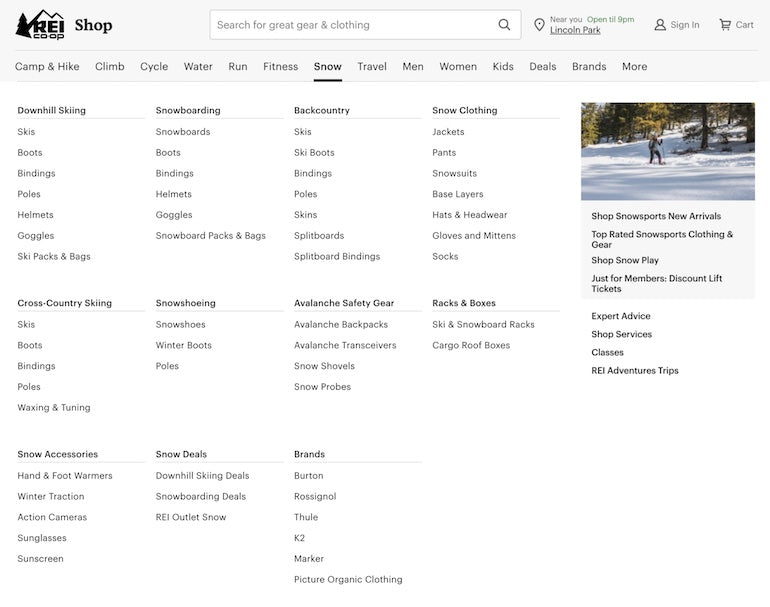
Nearly all of the organic search results are subcategory pages, so having a dedicated page for this keyword is highly useful from a search and likely user perspective. Using the same process as above, when you Google ‘boy’s corduroy pants,’ most of the pages ranking are product pages rather than subcategory pages. This means you could likely optimize a product for that keyword, and not need to build out a dedicated subcategory page.
Additional points to consider when trying to optimize for people and search engines include:
- Using a content hierarchy. This organizes your website pages through categories and subcategories. If you have more than a dozen products on a page, you could consider building out a subcategory page.
- Cross-linking between pages. SEO and content teams create useful blog posts, FAQs, and other content that can direct more traffic to product pages and vice versa. Horizontal linking easily navigates consumers to more information about your products and/or company, and also boosts your SEO efforts.
- No thinking required. Ultimately, navigating your website shouldn’t require much brain power. Your website should clearly guide users where to go.
You might also like: 10 Technical SEO Tips to Get the Most from an Ecommerce Website.
8. URL structure
Your URL structure should also be structured around your SEO strategy. Each URL slug should include only your web page or blog post’s focus keyword.
Make sure to do keyword research for each page you plan to include in your website design or redesign at launch. And do the same for every new page that you create along the way.
This helps Google understand what keyword(s) to rank your pages for, while also keeping your pages accessible. Because most focus keywords are only a few words, this ensures your URL slugs are easy to remember and type into a URL field if someone is looking for a specific page.
9. Metadata
Your metadata (or meta tags) includes things like your title tags and meta description. This is the information that appears in Google search results. Considering 36 percent of SEO experts think the title tag is the most important SEO element, make sure your metadata is optimized.
For example, here’s a Shopify search result:

The title tag and meta description should include your page or post’s focus keyword, further improving your SEO. Your title tag can have a maximum of 60 characters while your meta description can have a maximum of 160 characters.
10. Indexable content
If a search engine can easily crawl a site—easily exploring, reading, and understanding the content on each page of the site—then it’s considered an SEO-friendly site, and the probability of the pages appearing in the search engine results pages becomes much higher.
In order for the site to be crawlable, the main content on each page should be in HTML text format, since that is the easiest way for Google to understand what the page is about.
“If a search engine can easily crawl a site—easily exploring, reading, and understanding the content on each page of the site—then it’s considered an SEO-friendly site.”
One of the biggest challenges that web development and SEO teams run into is the use of JavaScript vs. HTML. HTML is great for Google but lacks the functionality that JavaScript brings, since sites are designed with various JavaScript frameworks like Angular, React, and more. Many developers therefore like to use JavaScript to make the site look and function a certain way.
However, all of these different JavaScript programs can cause issues for search engines, due to things like code errors, client-side rendering, etc. It takes Google a large amount of time to download, render (parse, compile, and execute JS code), fetch external resources, and then index that information. The more you add to your JS library, the more resources it takes Google to crawl and index that information. Both teams need to be aware of this fact, since all of this impacts site speeds and Google’s crawl budget.

Additionally, you should always check to see if Google is able to crawl and index the content on your site. A quick way to check to see if the site content can be seen is to run a quick search in Google using the exact text on a certain page.
If you copy and paste the text into Google and your site doesn’t show up, you need to troubleshoot the JavaScript coding to identify where the problem is, and work with the development team to find a good solution that allows Google to crawl and index your content.
Ultimately, users want a site that loads fast—40 percent of users are likely to abandon a site if it doesn’t load within three seconds. It’s in the best interest of both teams to create a site that looks good, has the information a user needs, and loads fast.
And yes, you can strike a balance between the need for JavaScript and the need for an SEO-friendly site. You can look into methods to make JavaScript work for your site without causing SEO issues, so everyone wins.
Walking the line between SEO and design
The key to a well-designed, SEO-friendly website is to bridge the gap between web development and SEO. Encourage your teams to work together from the beginning so your website is fully optimized for both SEO and usability.
Remember, providing value to your customer is the best way to rank in search engines. So optimize the elements above, write quality content, and design top-tier user experiences to improve your search results.
